What is Morbid Obesity?
Morbid obesity is a disease characterized by an increase in the natural energy stores, stored in the fat cells of the human body to a level that seriously increases the risk of mortality. Obesity is a serious global health problem characterized by endocrine (hormonal), metabolic and behavioral changes. In simple terms, it is the abnormal and excessive accumulation of fat in the human body to the extent that it impairs health, or in other words, more than 30% of body weight in adult women and more than 25% fat in men.
Morbid Obesity Surgery (Bariatric Surgery) is the general name for a variety of surgeries that help in weight loss. Surgical treatment is planned for patients who do not have a hormonal disorder, who cannot lose weight permanently with diet, exercise and medication. These patients are people between the ages of 18 and 60 who have an average of 40-50 kg more than normal weight (body-mass index more than 40kg / m2) and who do not have a medical condition that would preclude surgical treatment. The above methods are not aesthetic operations, but operations aimed at permanent weight loss characterised by changes in the size and absorption distance of the stomach and intestines.
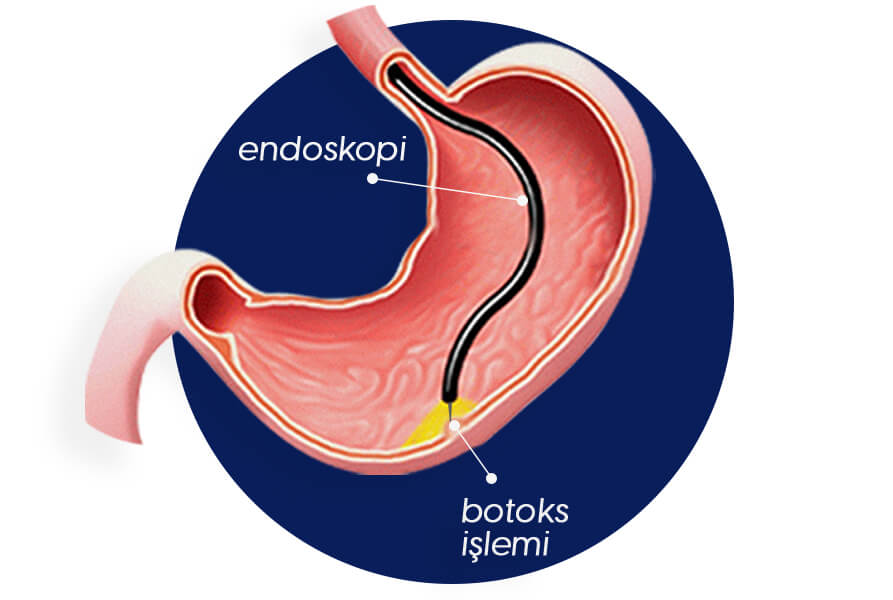
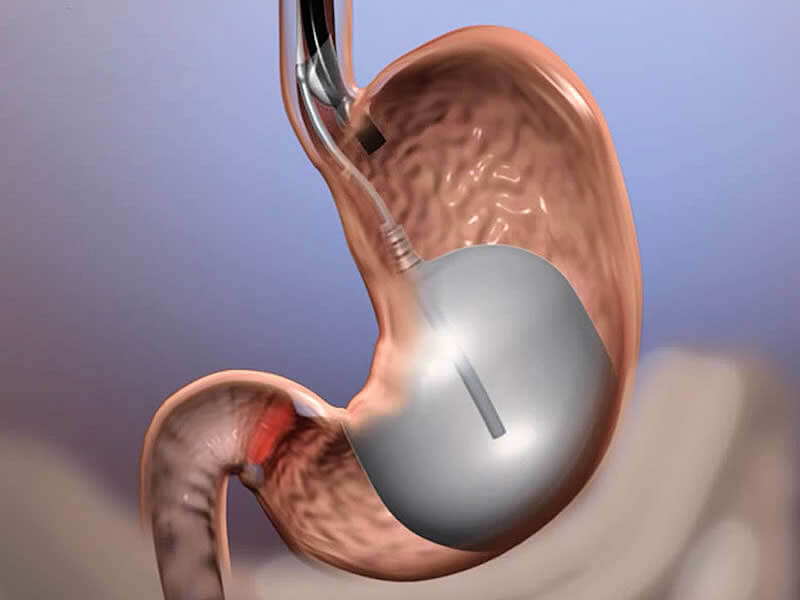
Gastric volume reduction surgery, also known as Sleeve Gastrectomy, aims to reduce the volume of the stomach (approximately 60-100 cc) so that the patient feels full with a very small amount of food. For this purpose, a certain part of the stomach is surgically removed, leaving a tubular stomach (about the size of a banana). The main effect of Sleeve Gastrectomy is to achieve early satiety by taking less food due to the small volume of the stomach.
Metabolic syndrome is a condition characterized by obesity, diabetes, high cholesterol and high blood pressure. The treatment of metabolic syndrome through surgical methods is called Metabolic Surgery. Type 2 diabetes is a multi-factorial, heterogeneous and dynamic spectrum of diseases. It is a health problem characterized not only by hormonal but also by neural, psychogenic and environmental factors. When classical treatment methods are not sufficient in type 2 diabetes, surgical treatment comes to the agenda.