It occurs with the uncontrolled proliferation of cells on the inner surface of the large intestine. It usually develops from benign growths called polyps. Colon cancer symptoms include abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea and bloody stools. With early diagnosis, the chance of treatment is high. Age, family history, eating habits and sedentary lifestyle are risk factors. Treatment usually includes surgery, chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
What are the symptoms of colon cancer?
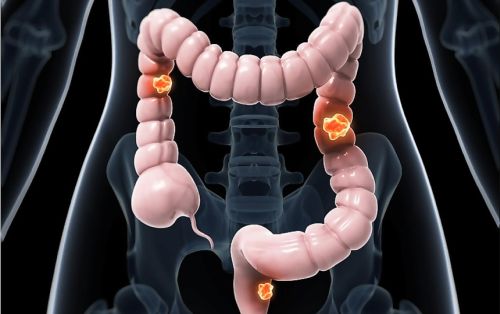 Changes in bowel habits, such as diarrhea or constipation. The shape or consistency of the stool may change. Blood in the stool or rectal bleeding. This may be light red or dark red blood. Constant or temporary pain in the abdominal area. These pains may be in the form of cramps. Unexplained weight loss. This can happen without a change in diet. Constant feeling of tiredness or weakness may be due to anemia. Bloating or discomfort in the abdominal area. Darkening or lightening of the color of the stool. Fatigue, paleness and weakness due to low iron levels. Severe abdominal pain, vomiting and difficulty passing stool. If one or more of these symptoms persist for a long time, it is important to see a healthcare professional. When colon cancer is diagnosed early, the chance of cure increases.
Changes in bowel habits, such as diarrhea or constipation. The shape or consistency of the stool may change. Blood in the stool or rectal bleeding. This may be light red or dark red blood. Constant or temporary pain in the abdominal area. These pains may be in the form of cramps. Unexplained weight loss. This can happen without a change in diet. Constant feeling of tiredness or weakness may be due to anemia. Bloating or discomfort in the abdominal area. Darkening or lightening of the color of the stool. Fatigue, paleness and weakness due to low iron levels. Severe abdominal pain, vomiting and difficulty passing stool. If one or more of these symptoms persist for a long time, it is important to see a healthcare professional. When colon cancer is diagnosed early, the chance of cure increases.
What Causes Colon Cancer?
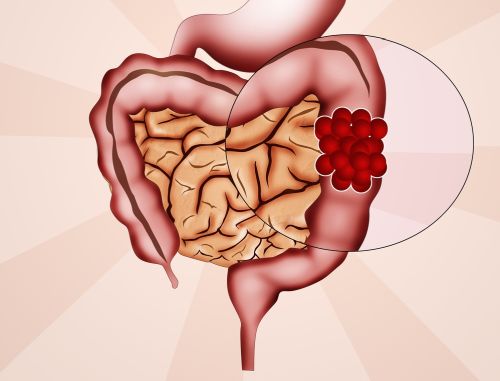 The risk increases in people with a family history of colon cancer. Additionally, certain gene mutations may also increase risk. The risk of development is higher in individuals over the age of 50. The risk of cancer increases as you get older. Consumption of high fat, red meat and processed meat may increase the risk. Consuming less fiber-rich foods may also increase this risk. Conditions such as chronic inflammatory bowel diseases, Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis increase the risk. Lack of physical activity, obesity, smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are other factors that increase the risk. Some types of polyps that develop in the intestine can turn into cancer over time. Apart from these factors, colon cancer can sometimes develop without any obvious cause. Regular screenings are especially important for people in risk groups. Because early diagnosis greatly increases the treatability of cancer.
The risk increases in people with a family history of colon cancer. Additionally, certain gene mutations may also increase risk. The risk of development is higher in individuals over the age of 50. The risk of cancer increases as you get older. Consumption of high fat, red meat and processed meat may increase the risk. Consuming less fiber-rich foods may also increase this risk. Conditions such as chronic inflammatory bowel diseases, Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis increase the risk. Lack of physical activity, obesity, smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are other factors that increase the risk. Some types of polyps that develop in the intestine can turn into cancer over time. Apart from these factors, colon cancer can sometimes develop without any obvious cause. Regular screenings are especially important for people in risk groups. Because early diagnosis greatly increases the treatability of cancer.
How Is Colon Cancer Diagnosed?
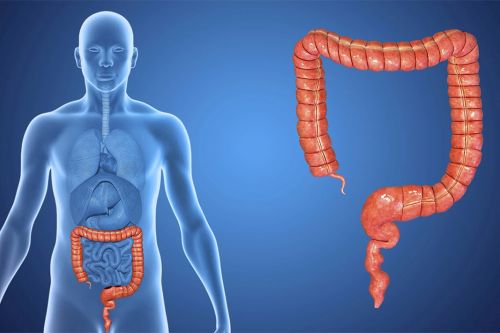 The doctor may ask about your family health history to assess your risk of colon cancer. Symptoms such as abdominal pain, weight loss, and blood in the stool are questioned. An abdominal examination is performed to check whether there is any abnormality. Tests may be performed to check for occult blood in the stool. These tests are useful in detecting early signs of cancer. Blood tests may be performed for symptoms of anemia. Additionally, some markers (for example, CEA) may indicate the presence of cancer. The inside of the large intestine is examined with a thin tube. The doctor uses this test to see polyps or abnormal growths. If necessary, a biopsy may be performed. A CT scan is used to obtain detailed images of the abdominal area. It is useful to evaluate the spread of tumors. MRI can be used in complex cases or when other imaging methods are inadequate. The tissue sample taken during colonoscopy or surgical intervention is examined in a laboratory environment. Biopsy is the most reliable method to make a definitive diagnosis. The biopsy result provides information about the presence, type and stage of cancer. This information is critical in determining the treatment plan. Early diagnosis of cancer is extremely important for the success of the treatment process. If you are experiencing symptoms of colon cancer, it is important to consult a healthcare professional.
Removing the tumor is the most common treatment method. The cancerous tissue is surgically removed along with the surrounding healthy tissue. If the tumor causes extensive tissue loss in part of the colon, a colostomy bag is used to remove part of the colon to the body surface. Medicines are used to stop cancer cells from growing and multiplying. It is usually applied after surgery to destroy residual cancer cells. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy may be used before surgery to reduce the size of the tumor. Radiation therapy aims to destroy cancer cells using high-energy rays. It can usually be used before or after surgery. Especially in cases where the tumor cannot be completely removed. Drugs that target specific molecular targets in cancer cells are used. This treatment may help stop cancer cells from growing. Immune system support, strengthens the body's immune system. It aims to create a more effective response against cancer cells. It can be especially applied for metastatic colon cancer. Opportunity to participate in clinical trials to test new treatment methods in the research phase. This may increase the treatment options available to patients. Regular check-ups are performed to monitor the condition of patients after treatment. Lifestyle changes are recommended to reduce the risk of developing cancer again. These treatment methods can often be used together. A special treatment plan is created according to the patient's condition. The treatment process of each patient is individual. It should be determined by a specialist oncologist.
The doctor may ask about your family health history to assess your risk of colon cancer. Symptoms such as abdominal pain, weight loss, and blood in the stool are questioned. An abdominal examination is performed to check whether there is any abnormality. Tests may be performed to check for occult blood in the stool. These tests are useful in detecting early signs of cancer. Blood tests may be performed for symptoms of anemia. Additionally, some markers (for example, CEA) may indicate the presence of cancer. The inside of the large intestine is examined with a thin tube. The doctor uses this test to see polyps or abnormal growths. If necessary, a biopsy may be performed. A CT scan is used to obtain detailed images of the abdominal area. It is useful to evaluate the spread of tumors. MRI can be used in complex cases or when other imaging methods are inadequate. The tissue sample taken during colonoscopy or surgical intervention is examined in a laboratory environment. Biopsy is the most reliable method to make a definitive diagnosis. The biopsy result provides information about the presence, type and stage of cancer. This information is critical in determining the treatment plan. Early diagnosis of cancer is extremely important for the success of the treatment process. If you are experiencing symptoms of colon cancer, it is important to consult a healthcare professional.
Removing the tumor is the most common treatment method. The cancerous tissue is surgically removed along with the surrounding healthy tissue. If the tumor causes extensive tissue loss in part of the colon, a colostomy bag is used to remove part of the colon to the body surface. Medicines are used to stop cancer cells from growing and multiplying. It is usually applied after surgery to destroy residual cancer cells. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy may be used before surgery to reduce the size of the tumor. Radiation therapy aims to destroy cancer cells using high-energy rays. It can usually be used before or after surgery. Especially in cases where the tumor cannot be completely removed. Drugs that target specific molecular targets in cancer cells are used. This treatment may help stop cancer cells from growing. Immune system support, strengthens the body's immune system. It aims to create a more effective response against cancer cells. It can be especially applied for metastatic colon cancer. Opportunity to participate in clinical trials to test new treatment methods in the research phase. This may increase the treatment options available to patients. Regular check-ups are performed to monitor the condition of patients after treatment. Lifestyle changes are recommended to reduce the risk of developing cancer again. These treatment methods can often be used together. A special treatment plan is created according to the patient's condition. The treatment process of each patient is individual. It should be determined by a specialist oncologist.


