The surgical removal of the gallbladder from the body. It is usually performed due to problems such as gallstones or inflammation. It is performed laparoscopically by making small incisions in the abdomen. Patients generally recover quickly after gallbladder surgery. The digestive system continues to function normally without the gallbladder. The surgery is performed to relieve pain and prevent complications.
When is Gallbladder Surgery Performed?
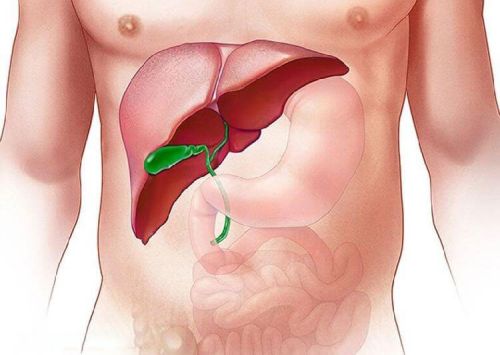 The formation of stones in the gallbladder is the most common reason for surgery. Gallstones can block the bile ducts, causing pain, inflammation, and infection. In this case, the gallbladder is usually removed. When the gallbladder is inflamed (acute cholecystitis), removal of the organ is usually recommended. Surgery is necessary if symptoms like pain, fever, and nausea are severe. If polyps are found in the gallbladder, especially large ones, surgery is required due to the risk of cancer. In rare cases of diagnosed gallbladder cancer, removing the gallbladder is crucial. Gallbladder surgery may be necessary when gallstones block the bile ducts, causing obstruction. In such cases, the gallbladder is usually removed laparoscopically. The surgery is performed to relieve symptoms and prevent serious complications.
The formation of stones in the gallbladder is the most common reason for surgery. Gallstones can block the bile ducts, causing pain, inflammation, and infection. In this case, the gallbladder is usually removed. When the gallbladder is inflamed (acute cholecystitis), removal of the organ is usually recommended. Surgery is necessary if symptoms like pain, fever, and nausea are severe. If polyps are found in the gallbladder, especially large ones, surgery is required due to the risk of cancer. In rare cases of diagnosed gallbladder cancer, removing the gallbladder is crucial. Gallbladder surgery may be necessary when gallstones block the bile ducts, causing obstruction. In such cases, the gallbladder is usually removed laparoscopically. The surgery is performed to relieve symptoms and prevent serious complications.
How is Gallbladder Surgery Performed?
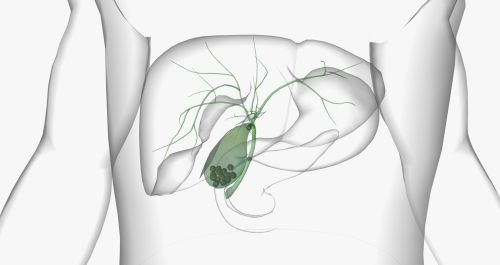 The patient is put under general anesthesia. The abdominal area is cleaned sterilely. In the laparoscopic method, it is performed with small incisions and the gallbladder is reached with the help of a camera. In open surgery, the abdomen is opened with a larger incision to reach the gallbladder. In the laparoscopic method, generally 3-4 small incisions are made in the abdominal wall. In open surgery, an incision of about 10-15 cm is made in the upper right abdomen. The gallbladder is carefully separated from the area where it is attached to the liver. The bile ducts and vessels are carefully cut and clipped. In the laparoscopic method, the gallbladder is removed through one of the small incisions. In the open method, it is removed through the large incision. The surgical site is checked for bleeding. If necessary, a drain is placed in the surgical area. The incisions are closed with stitches. The laparoscopic method leaves smaller and more aesthetic scars. The patient is awakened and monitored. The hospital stay is usually 1-2 days in the laparoscopic method, but this period may be longer in open surgeries. These steps encompass the general procedure of gallbladder surgery.
The patient is put under general anesthesia. The abdominal area is cleaned sterilely. In the laparoscopic method, it is performed with small incisions and the gallbladder is reached with the help of a camera. In open surgery, the abdomen is opened with a larger incision to reach the gallbladder. In the laparoscopic method, generally 3-4 small incisions are made in the abdominal wall. In open surgery, an incision of about 10-15 cm is made in the upper right abdomen. The gallbladder is carefully separated from the area where it is attached to the liver. The bile ducts and vessels are carefully cut and clipped. In the laparoscopic method, the gallbladder is removed through one of the small incisions. In the open method, it is removed through the large incision. The surgical site is checked for bleeding. If necessary, a drain is placed in the surgical area. The incisions are closed with stitches. The laparoscopic method leaves smaller and more aesthetic scars. The patient is awakened and monitored. The hospital stay is usually 1-2 days in the laparoscopic method, but this period may be longer in open surgeries. These steps encompass the general procedure of gallbladder surgery.
Precautions After Gallbladder Surgery
 After surgery, fatty foods can cause digestive difficulties. It is important to start with light, fat-free, and easy-to-digest foods. Eating small and frequent meals can ease digestion. It is necessary to drink enough water to support the digestive system and keep the body hydrated. Fluid intake is particularly important in the period after gallbladder surgery. Heavy physical activities should be avoided for the first few days. Slow walks and light exercises can improve circulation and contribute to the healing process. However, heavy lifting should be avoided for the duration recommended by the doctor. Pain relievers and other medications prescribed by the doctor should be taken regularly. If antibiotic treatment is applied to prevent the risk of infection, this treatment should be carefully followed. It is important to keep the stitches clean and perform regular dressing to reduce the risk of infection. Any redness, swelling, or pain should be reported to the doctor. Immobility and some medications after surgery can cause constipation. Drinking plenty of water, consuming fiber-rich foods, and using a mild laxative as advised by the doctor can prevent this issue. It is important not to miss periodic doctor check-ups after the surgery. These check-ups are necessary to evaluate the progress of the healing process. Paying attention to these basic recommendations is crucial. By doing so, you can get through the post-gallbladder surgery period more comfortably and quickly.
After surgery, fatty foods can cause digestive difficulties. It is important to start with light, fat-free, and easy-to-digest foods. Eating small and frequent meals can ease digestion. It is necessary to drink enough water to support the digestive system and keep the body hydrated. Fluid intake is particularly important in the period after gallbladder surgery. Heavy physical activities should be avoided for the first few days. Slow walks and light exercises can improve circulation and contribute to the healing process. However, heavy lifting should be avoided for the duration recommended by the doctor. Pain relievers and other medications prescribed by the doctor should be taken regularly. If antibiotic treatment is applied to prevent the risk of infection, this treatment should be carefully followed. It is important to keep the stitches clean and perform regular dressing to reduce the risk of infection. Any redness, swelling, or pain should be reported to the doctor. Immobility and some medications after surgery can cause constipation. Drinking plenty of water, consuming fiber-rich foods, and using a mild laxative as advised by the doctor can prevent this issue. It is important not to miss periodic doctor check-ups after the surgery. These check-ups are necessary to evaluate the progress of the healing process. Paying attention to these basic recommendations is crucial. By doing so, you can get through the post-gallbladder surgery period more comfortably and quickly.


